You have already completed the exam before. Hence you can not start it again.
Exam is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the exam.
You must first complete the following:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), ( 0 )
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0 , ( 0 )
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0 )
If you scored less than 80%, take more practice tests to ensure you pass your exam. More Practice Tests from BoostPrep.com
The anatomy of the airway consists of the upper and lower airways. The upper airway starts at the mouth and nares and ends at the _________?
To create negative pressure in the thorax (chest cavity) the diaphragm contracts and moves _____________. This action expands the volume of the thorax, allowing air to rush into the lungs.
You are transporting a 48-year-old male patient between medical facilities… While obtaining the patient’s history, you learn that the patient was involved in a fall at work and suffered a hip fracture and a head injury. The patient is now presenting with labored breathing at 30/min that has progressively worsened over the last 24 hours, a heart rate of 104, and a blood pressure of 98/70. On auscultation, you hear diffuse rales. The patient denies any complaints of pain other than those related to his recent fall. What is the most likely cause of the patient’s respiratory distress?
You are dispatched to a residence of a 46-year-old female patient complaining of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramping. She states that the onset occurred shortly after eating some cheesecake. Her only medical history is lactose intolerance. Her blood pressure is 136/88 mm Hg. Her radial pulse is 94 beats per minute and her respiratory rate is 18 breaths per minute. She vomited two times prior to your arrival. From what condition is this patient most likely suffering?
Your patient is a 32-year-old male who was complaining of a severe, crushing feeling in the center of his chest and shortness of breath that began while he was mowing his lawn 45 minutes prior to your arrival. He is now only responding to painful stimuli. Presently, his minute ventilation is still adequate, his pulse oximeter reads 95% on room air, and you find his skin to be pale, cool, and diaphoretic. What would be your initial action?
Your patient has a laceration to the right leg, intersecting the femoral artery. You have applied direct pressure to the wound, but it continues to soak through the bandages. What should you do next?
Your trauma patient has her left hand caught between rollers on a conveyor belt. Extrication takes 30 minutes. Evaluation of the injury during extrication showed delayed capillary refill distal to the injury. Post extrication shows rapid capillary refill distal to the injury deformity mid-palm. There are no obvious fractures, lacerations, or minor swelling. Knowing that crush injuries can cause many other problems, which is not considered a complication of crush injury?
Your 16-year-old trauma patient has what appears to be a mid-shaft femur fracture. You notice a laceration directly over the suspected fracture, and bleeding is controlled. What type of fracture would this be?
Food poisoning may be difficult to diagnose in the field due to its broad range of symptoms and the time it takes to make the patient ill. All of the following are types of food-borne illnesses except which one?
You arrive on the scene at a private residence to find a patient with an altered mental status. You quickly scan the home. Which of the following items will help point you in the right direction to find the cause of the altered mental status?
Your patient is not responding to loud verbal stimuli. You find the following medications: Glucophage and Lipitor. What is the likely cause of the patient’s unresponsiveness?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) has the following signs and symptoms: Acetone on breath, dry skin, poor skin turgor, altered mental status, confusion, thirst, and frequent urination. What other symptoms are associated with DKA?
Stroke symptoms often present the same as other medical problems. Working through the differentials is a must to prevent improper treatment for the signs and symptoms. Hypoglycemia is often mistaken for a CVA. How can an EMT rule in or out this differential?
You are dispatched to the scene of a 9-year-old female who has been struck by a car. Police are unable to reach her parents. What gives you the ability to treat the patient?
You are dispatched to 123 Somewhere Rd. to a call for an injured woman. As you approach the home, a man opens the door and tells you, “This is none of your business. Get out of here.” What is the best course of action in this case?
While responding to a hazardous materials incident, the EMT should approach the scene from _________?
Prepare for your EMT exam with our partner, BoostPrep. They offer 8 full-length exams, 1,000+ practice questions, 580+ flashcards, & more.
The National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) is a non-profit organization that helps ensure the skills, knowledge, and expertise of Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs) in the United States.
The NREMT administers a wide range of emergency medical professional tests, including:
Though the exams vary based on the type of emergency responder, they all cover the general knowledge and skills required to provide emergency medical services.
You can read our NREMT test overview for more information on each exam.
Fast Facts:
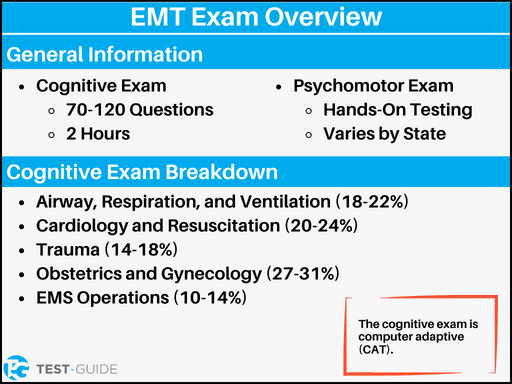
There will be 2 portions on your EMT test:
The cognitive portion consists of multiple-choice questions. You will have 2 hours to complete the exam.
The psychomotor portion will ask you to perform various emergency skills in a hands-on environment.
The cognitive exam consists of multiple-choice questions. The exam is a computer adaptive test, which means the questions get harder or easier depending on how you answered the previous question.
The questions will cover 5 different categories. Each of the categories (except EMS Operations) will be further split into Adult (85%) and Pediatric (15%) questions.
For more information, visit the official website.
The psychomotor exam consists of you performing various emergency medical skills in front of an instructor.
At the EMT level, the psychomotor exam is administered by the state EMS office or by an educational institution approved by the state.
With this being the case, the psychomotor exam will vary from state to state. Some concepts you should be familiar with include:

Before you can sit for the EMT exam, you will need to meet the following requirements:
You can follow these steps to register for your EMT test:
For more information, you can review the official EMT candidate handbook. We recommend answering some of the NREMT practice questions above before registering for your exam.
Since the exam is computer adaptive, the scoring of the exam is not as straight-forward as you would think.
Not all students receive the same number of questions. The questions are weighted, with the harder questions being worth more points.
There is not technically a passing score. The exam will continue feeding you questions (up to 120 total) until it is 95% certain that your abilities are above a passing level.
Some individuals may reach this 95% certainty at question 87, while other students may not reach this point until question 110.
When it comes to EMT test prep, everyone has different needs, timelines, and study habits. We have listed some tips to help you succeed when studying.
We recommend using NREMT practice tests to start your studies. This will help you gauge where you stand.
If you do really well on your first exam, then you may be able to consider yourself ready for the actual exam. If you struggle, you can come up with a plan to study and can create an EMT study guide.
Take our free EMT practice test above to get started!
After taking your first exam, analyze your results. We break down all of our practice exams by the exact categories tested on the actual exam.
By analyzing your results, you can see which categories give you the most trouble and focus your studies on those specific categories.
For example, if you struggled the most with EMS operations, you could focus your studies on that subject.
Reviewing the answer explanations plays a huge role in your EMT test prep. We provide in-depth answer explanations to every single question.
Our answer explanations will help you understand complex concepts and learn why an answer is correct or incorrect. By reviewing answer explanations, you will learn key concepts that will be tested on the actual exam.
Flashcards are a great study tool to utilize when preparing for the EMT. We recommend using flashcards for things like:
By using flashcards, you will become familiar with core concepts that will help you do better on the actual exam (and be helpful in your career as an EMT).